Table of Contents
Nutrition plays a crucial role in maintaining physical health, but its impact on mental health is equally significant. The foods we consume directly affect our brain function, influencing our mood, energy levels, and overall mental well-being. By understanding the connection between diet and mental health, we can make informed choices to support a healthier, happier mind.
Understanding the Gut-Brain Connection
The gut-brain connection, often referred to as the gut-brain axis, highlights the intricate relationship between our digestive system and brain. The gut is home to trillions of microorganisms that form the gut microbiome, which plays a vital role in digestion, immune function, and even mood regulation. The gut and brain communicate through neural pathways, hormonal signals, and the immune system, influencing each other continuously.
The Role of Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that transmit signals in the brain and play a key role in mood regulation. Serotonin, often called the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, is primarily produced in the gut. The foods we eat can influence the production and function of neurotransmitters, affecting our mood and mental state.

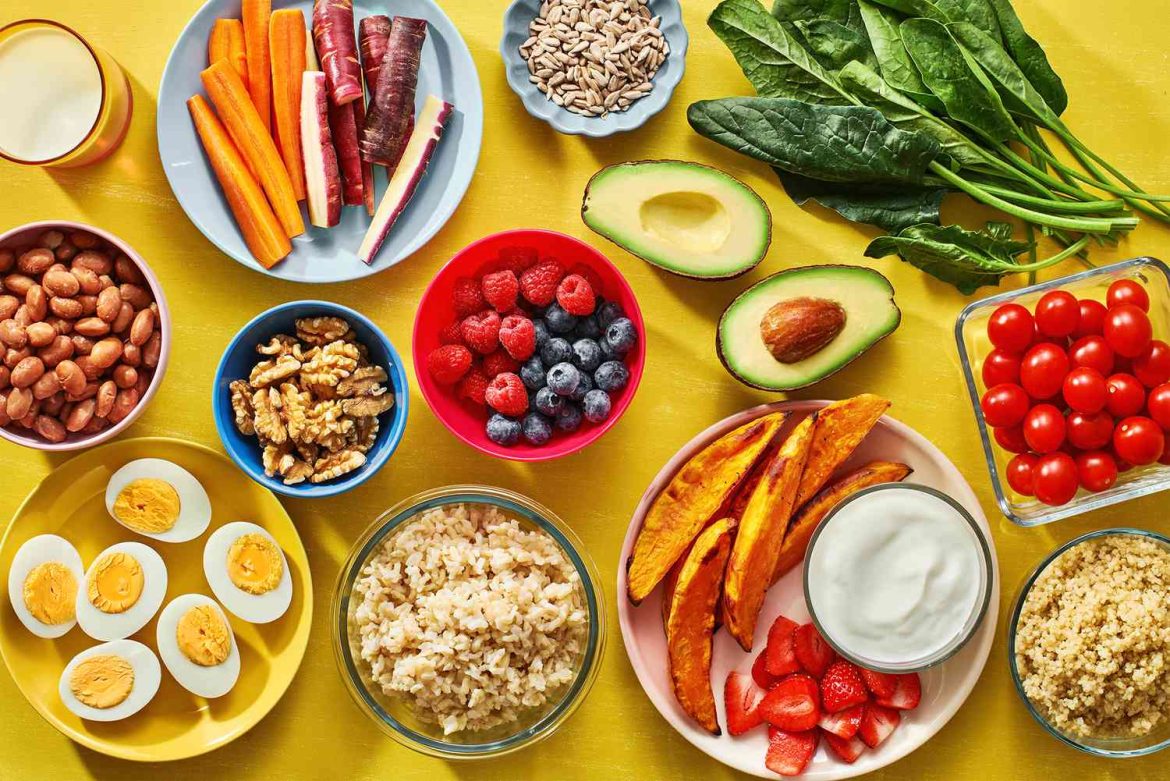
Key Nutrients for Mental Health
Certain nutrients are essential for brain health and can positively impact mood and cognitive function. Incorporating these nutrients into your diet can help boost your mental well-being.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are crucial for brain health. They help build cell membranes in the brain, reduce inflammation, and support neurotransmitter function. Studies have shown that omega-3 fatty acids can reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, and improve overall mood.
Foods Rich in Omega-3s:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Flaxseeds
- Chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Algal oil (a plant-based source)
B Vitamins
B vitamins, particularly B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are vital for brain function and the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. Deficiencies in these vitamins are linked to mood disorders, including depression.
Foods Rich in B Vitamins:
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Whole grains (brown rice, oats)
- Legumes (beans, lentils)
- Eggs
- Meat and poultry

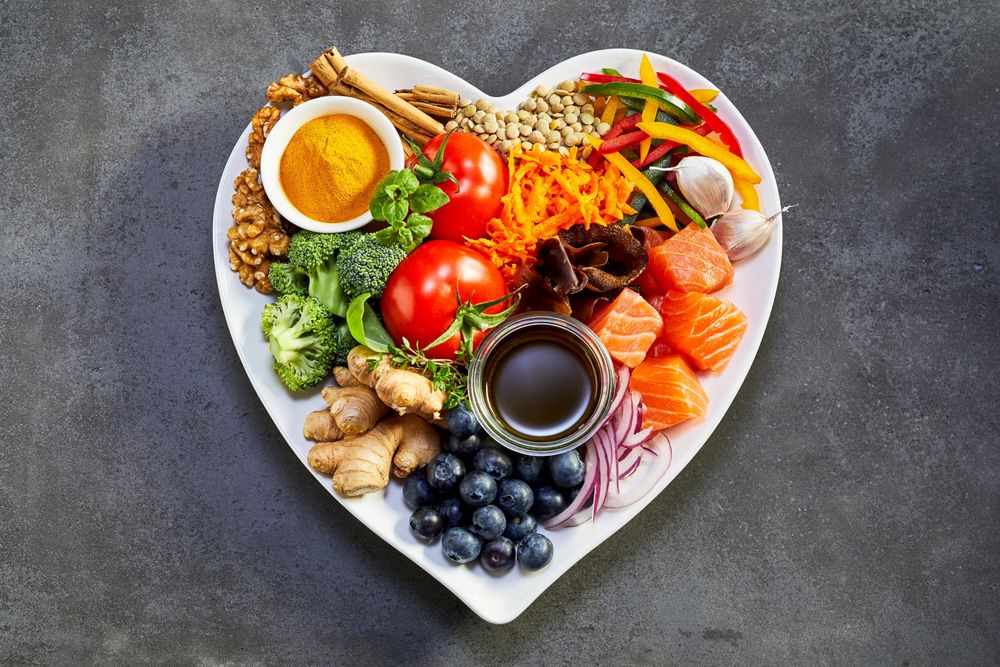
Vitamin D
Vitamin D, often called the “sunshine vitamin,” is important for mood regulation. Low levels of vitamin D are associated with an increased risk of depression and seasonal affective disorder (SAD). Sun exposure is a primary source of vitamin D, but it can also be obtained through certain foods.
Foods Rich in Vitamin D:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel)
- Egg yolks
- Fortified dairy products
- Mushrooms exposed to sunlight
Antioxidants
Antioxidants, found in fruits and vegetables, protect the brain from oxidative stress, which can damage brain cells and contribute to mental health disorders. Antioxidant-rich foods help reduce inflammation and promote overall brain health.
Foods Rich in Antioxidants:
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries)
- Dark chocolate
- Nuts (almonds, walnuts)
- Green tea
- Colorful vegetables (bell peppers, carrots)
Probiotics
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that support a healthy gut microbiome. A balanced gut microbiome is linked to better mental health, as it influences the production of neurotransmitters and reduces inflammation. Fermented foods are a great source of probiotics.
Foods Rich in Probiotics:
- Yogurt
- Kefir
- Sauerkraut
- Kimchi
- Miso
Incorporating Mood-Boosting Foods into Your Diet
To support your mental health through nutrition, focus on a balanced diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods. Here are some tips to incorporate mood-boosting foods into your daily meals:
Start with a Nutritious Breakfast
A healthy breakfast sets the tone for the day and can help stabilize your mood and energy levels. Include foods rich in protein, fiber, and healthy fats, such as Greek yogurt with berries and nuts, or whole-grain toast with avocado and a poached egg.
Snack Smart
Choose snacks that provide sustained energy and support brain health. Options like a handful of walnuts, a piece of dark chocolate, or carrot sticks with hummus are nutritious and satisfying.
Include Omega-3s in Your Meals
Incorporate fatty fish into your diet at least twice a week. If you’re vegetarian or vegan, add flaxseeds, chia seeds, or algal oil to smoothies, salads, or oatmeal.
Eat a Rainbow of Fruits and Vegetables
Aim for a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables to ensure you’re getting a broad range of antioxidants and nutrients. Add berries to your breakfast, leafy greens to your lunch, and a mix of roasted vegetables to your dinner.
Prioritize Whole Grains and Legumes
Whole grains and legumes provide essential B vitamins and fiber. Include options like quinoa, brown rice, lentils, and chickpeas in your meals to support brain health and digestion.
Conclusion
Nutrition plays a vital role in mental health, and the foods we choose can significantly impact our mood and cognitive function. By understanding the connection between diet and mental well-being, and incorporating nutrient-rich, mood-boosting foods into our daily routine, we can support a healthier, happier mind. Remember, a balanced diet, combined with other healthy lifestyle practices, is key to achieving optimal mental health.


